Technology and robotics are advancing and will reduce the need for workers in the future.
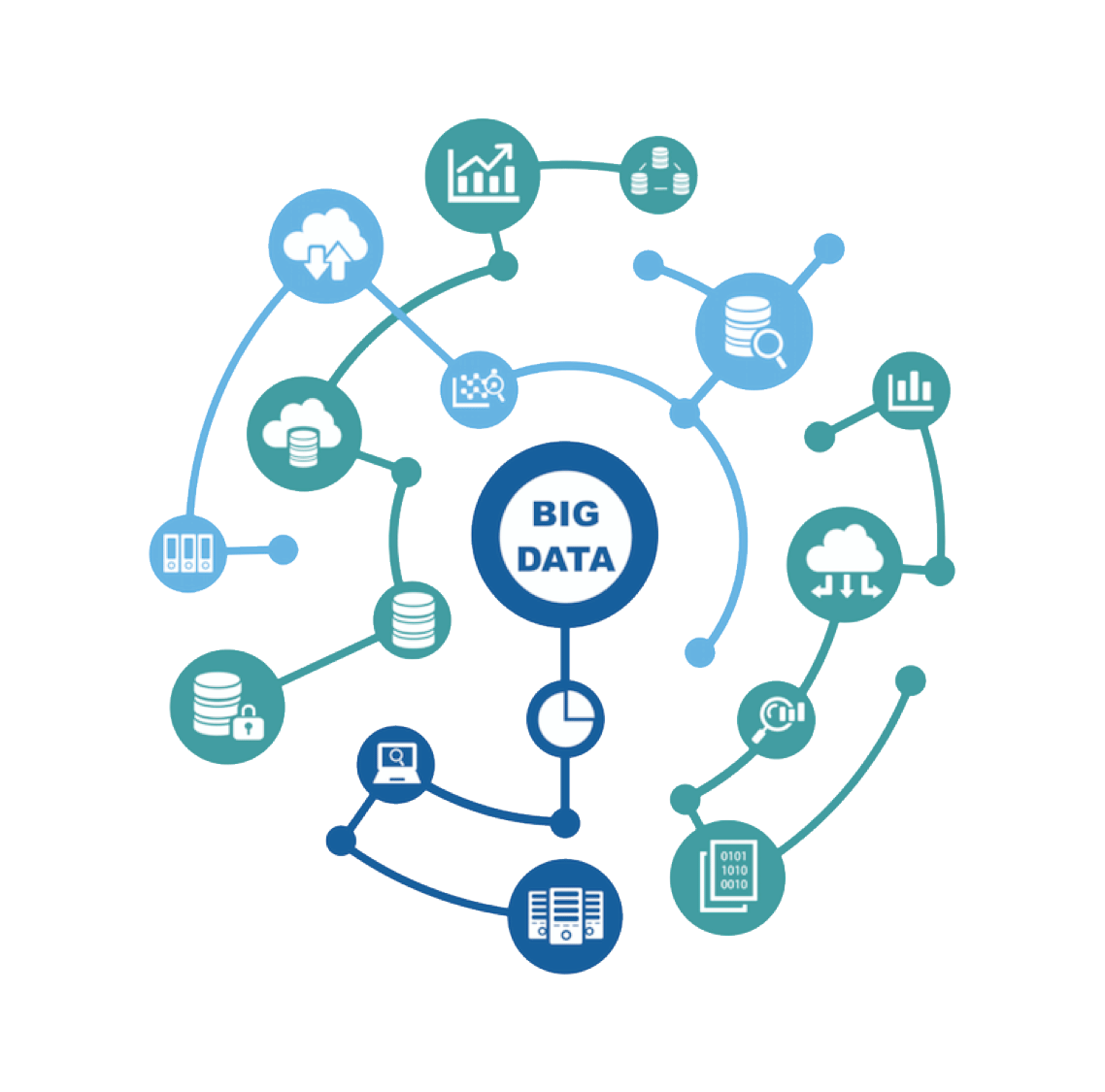
Big data tends to refer to the use of predictive analytics, user behavior analytics, or certain other advanced data analytics methods that extract value from big data, and seldom to a particular size of data set.HHealthcare, Education are domains that we have used for data analytics.
Remote monitoring in the healthcare industry is now possible thanks to Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled gadgets, which have the potential to keep patients safe and healthy while also empowering clinicians to provide superior treatment. Patient engagement and satisfaction have also increased as contacts with doctors have gotten easier and more efficient. Furthermore, remote monitoring of a patient's health helps to shorten hospital stays and avoid readmissions. IoT also has a huge impact on lowering healthcare expenses and increasing treatment outcomes.
The Internet of Things is undeniably changing the healthcare business by rethinking the space of devices and human contact in the delivery of healthcare solutions. Patients, families, physicians, hospitals, and insurance companies all benefit from IoT applications in healthcare.

Cloud Platforms / Cloud computing architecture refers to the components and subcomponents required for cloud computing. These components typically consist of a front end platform (fat client, thin client, mobile ),back end platforms (servers, storage), a cloud based delivery, and a network (Internet, Intranet, Intercloud). Combined, these components make up cloud computing architecture. Software as a service (SaaS), Platform as a service (PaaS), Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)

Mobile app development is the act or process by which a mobile app is developed for mobile devices, such as personal digital assistants, enterprise digital assistants, or mobile phones. These software applications are designed to run on mobile devices, such as a smartphone or tablet computers. These applications can be pre-installed on phones during manufacturing platforms, or delivered as web applications using server-side or client-side processing (e.g., JavaScript) to provide an "application-like" experience within a web browser. Application software developers also must consider a long array of screen sizes, hardware specifications, and configurations because of intense competition in mobile software and changes within each of the platforms.

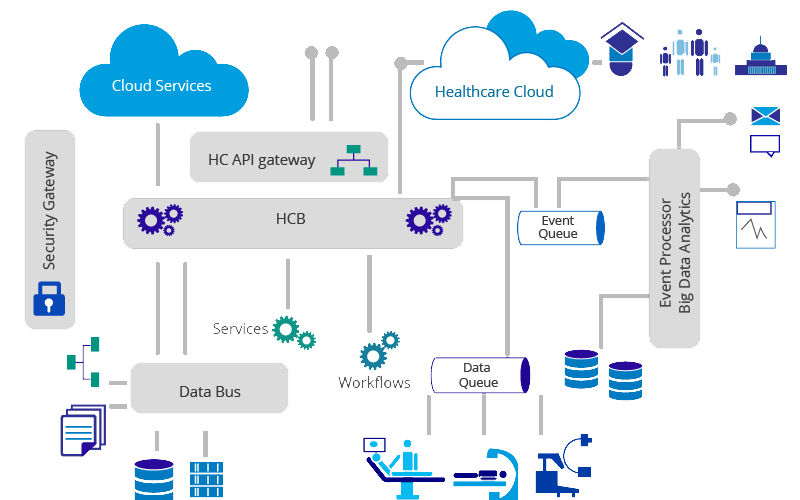
Cloud architecture is the way technology components combine to build a cloud, in which resources are pooled through virtualization technology and shared across a network. The components of a cloud architecture include:
Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS architecture providers deliver and maintain applications and software to organizations over the Internet, thereby eliminating the need for end users to deploy the software locally. SaaS applications are typically accessed via a web interface available from a broad variety of devices and OSes.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): In this cloud model, the service provider offers a computing platform and solution stack, often including middleware, as a service. Organizations can build upon that platform to create an application or service. The cloud service provider delivers the networks, servers, and storage required to host an application while the end user oversees software deployment and configuration settings.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): In this, cloud at its simplest form, a third-party provider eliminates the need for organizations to purchase servers, networks, or storage devices by providing the necessary infrastructure. In turn, organizations manage their software and applications and only pay for the capacity they need at any given time.
Up-front planning: Ensure there is an understanding of capacity needs when designing a cloud architecture. As organizations begin to build out architecture, continuously test performance to avoid experiencing unexpected glitches in production.
Security first: Protect clouds from hackers and unauthorized users by safeguarding all layers within a cloud infrastructure with data encryption, patch management, and rigid policies. Consider zero-trust security models for the highest levels of security across the hybrid, multi-cloud enterprise.
Ensure disaster recovery: Automate recovery processes to avoid costly downtime and ensure a speedy recovery from service disruptions. Monitoring capacity and using a redundant network can also ensure a highly available architecture.
Maximize performance: Leverage and manage the right compute resources by continuously monitoring business demands and technology needs.
Cut costs: Take advantage of automated processes, managed service providers, and utilization tracking to eliminate unnecessary cloud computing expenses.

Cloud-native computing is an approach in software development that utilizes cloud computing to "build and run scalable applications in modern, dynamic environments such as public, private, and hybrid clouds". Technologies such as containers, microservices, serverless functions, and immutable infrastructure, deployed via declarative code are common elements of this architectural style. These techniques enable loosely coupled systems that are resilient, manageable, and observable. Combined with robust automation, they allow engineers to make high-impact changes frequently and predictably with minimal toil. Frequently, cloud-native applications are built as a set of microservices that run in Docker containers, and may be orchestrated in Kubernetes and managed and deployed using DevOps and Git CI workflows(although there is a large amount of competing open source that is supports cloud-native development). The advantage of using Docker containers is the ability to package all software needed to execute into one executable package. The container runs in a virtualized environment, which isolates the contained application from its environment.

Chatbots are computer programmes that use machine learning algorithms, such as natural language processing (NLP), to initiate and maintain conversations with users in order to provide real-time support to patients.